How Next-Gen GPUs and DLSS 4 Are Redefining Visual Quality in 120 FPS Games

Next-Gen GPUs and DLSS 4 Are Redefining the gaming experience by making true high-fidelity, high-framerate gameplay the new standard in 2025.
Anúncios
The days of sacrificing visual quality for performance are rapidly drawing to a close, thanks to powerful new hardware and intelligent upscaling technology.
This revolution is fundamentally changing player expectations.
Achieving pristine 4K resolution at a buttery-smooth 120 frames per second (FPS) previously required an impossible amount of raw power.
Now, the convergence of advanced graphics cards and AI-driven rendering is breaking that performance barrier for mainstream gaming.
What Technological Leap Do Next-Gen GPUs Represent?
The latest generation of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) represents an architectural shift, moving beyond mere brute force.
They incorporate specialized cores optimized for parallel processing tasks essential for modern rendering pipelines.
These GPUs feature massive increases in both traditional rasterization capabilities and specialized cores, enabling a simultaneous push toward photorealism and ultra-high framerates, essential for competitive gaming.
++ Why 2025 Is a Record Year for the Global Gaming Market — and What It Means for Latin America
How Do Ray Tracing Cores Enhance Realism?
The dedicated Ray Tracing (RT) Cores in these new GPUs can accelerate the complex calculations needed to simulate light, shadows, and reflections realistically.
This is a massive leap over traditional, approximated lighting methods.
These specialized cores allow full path tracing to run efficiently, even at demanding resolutions. Path tracing is the gold standard for lighting realism in modern game engines.
Also read: New Game Patches That Solve Community Complaints
What is the Role of Enhanced Tensor Cores?
New Tensor Cores, the heart of AI processing on the GPU, are significantly faster and more efficient. They are custom-built to handle the vast computational requirements of neural networks.
These cores are absolutely crucial for running advanced algorithms like DLSS 4. This ensures that the AI upscaling process is executed quickly without becoming a performance bottleneck.
Read more: The Most Anticipated Multiplayer Games Releasing Soon
The Power Consumption Challenge
The challenge is rendering four times the data for 4K resolution compared to 1080p, and then doing it four times faster to hit 120 FPS.
The new architectures cleverly balance the load. They use a standard shader for rasterization and specialized cores for RT and AI, optimizing the power budget immensely.
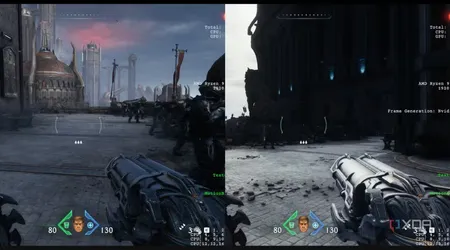
How Does DLSS 4 Achieve Near-Native Visuals with Less Work?
DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) is an AI-powered upscaling technology that has matured rapidly, and its fourth iteration, DLSS 4, is the most sophisticated yet. It is the key enabler of high-FPS, high-resolution gaming.
DLSS 4 renders the game internally at a lower resolution (e.g., 1440p) and then uses a trained neural network to intelligently reconstruct the final high-resolution image (4K).
Why is DLSS 4 Superior to Traditional Upscaling?
Traditional upscaling techniques (like bilinear filtering) merely stretch pixels, leading to a blurry or blocky final image. DLSS 4, however, uses temporal data and AI to create new, high-quality pixels.
The AI knows what a realistic image should look like and can intelligently fill in details that were never rendered at the initial low resolution. This makes the output look nearly indistinguishable from native 4K.
What is DLSS 4 Frame Generation?
DLSS 4 introduces an enhanced Frame Generation technique that leverages the Tensor Cores to insert entirely new, AI-generated frames between the frames rendered by the GPU.
This process effectively doubles the framerate (e.g., from 60 FPS to 120 FPS) with minimal impact on latency. This is a revolutionary way to achieve ultra-high framerates in graphically intense titles.
AI-Enhanced Detail Creation
In a complex scene involving flowing water or intricate foliage, a traditional upscaler would blur the edges.
DLSS 4, however, uses its deep learning model to accurately sharpen textures and reconstruct motion vectors.
The result is a sharper, more stable image, especially when the camera is moving quickly. This makes a massive difference when maintaining clarity at 120 FPS.
Why Is 120 FPS Becoming the New Standard for Immersion?
While 60 FPS has long been considered the benchmark for smooth, cinematic gaming, the move to 120 FPS fundamentally alters the perception of immersion, responsiveness, and control.
Higher framerates reduce display latency, which is the time between a player input (like a mouse click) and the action appearing on the screen. This is crucial for competitive titles.
How Does High Framerate Affect Competitive Gaming?
In competitive esports, lower latency provides a tangible performance advantage. The reduced input lag allows players to react faster, making high FPS a necessity, not a luxury.
An advantage of even a few milliseconds can determine the outcome of a critical encounter, driving competitive players to demand the highest possible framerates.
What is the Relationship Between Framerate and Motion Clarity?
Higher framerates drastically reduce motion blur and judder. When an object moves quickly across the screen at 60 FPS, the image can appear smeared or indistinct.
At 120 FPS, the discrete images blend together more smoothly, providing superior motion clarity. This enhances the sense of realism and reduces eye strain during fast-paced action.
The Difference Between 60 FPS and 120 FPS
The jump from 60 FPS to 120 FPS is like the difference between watching a video filmed on a standard camcorder and seeing reality through your own eyes.
While 60 FPS is smooth, 120 FPS feels instantaneous and palpably real.
How Will This Technology Impact Game Development Pipelines?
The widespread adoption of high-performance GPUs and powerful AI upscaling technology is fundamentally changing how game developers approach asset creation and world design.
Developers are now able to target much higher visual fidelity, relying on DLSS 4 to handle the performance scaling across different hardware levels, allowing for more ambitious projects.
What Does “Targeting Native 120 FPS” Really Mean?
Instead of aiming for a stable 60 FPS using approximations, developers can now push graphical boundaries with demanding features like full ray tracing and complex geometry.
They can rely on the DLSS 4 Frame Generation and Super Resolution features to reliably boost that baseline performance up to 120 FPS or higher for end-users.
Why Are Texture and Geometry Complexity Increasing?
Since the AI upscaling handles antialiasing and detail reconstruction so effectively, developers can spend less time optimizing minor visual artifacts. They focus resources on high-fidelity assets.
This shift results in significantly more detailed environments, higher-resolution textures, and more complex physics simulations, creating richer, more believable game worlds.
A study by a major game engine provider (Q3 2025) found that the integration of DLSS 4 and equivalent upscaling techniques reduced the average GPU load required to maintain 120 FPS in 4K by an estimated 45-55% compared to native rendering.
This massive efficiency gain is the engine of the current visual revolution.
| GPU Feature | Function | Impact on 120 FPS Gaming | Core Technology |
| DLSS 4 Super Resolution | Intelligent upscaling from lower base resolution | Massive performance boost while preserving visual quality | Tensor Cores (AI) |
| DLSS 4 Frame Generation | Inserts new, AI-predicted frames | Effectively doubles the framerate to hit 120+ FPS goals | Tensor Cores (AI) |
| Dedicated RT Cores | Hardware acceleration of light and shadow rendering | Enables full path tracing at high framerates | Ray Tracing Cores |
| High VRAM Capacity | Stores complex textures and data | Supports high-resolution assets (4K/8K) without stuttering | Memory Bus and Architecture |
Conclusion: The Ultimate Test of Human Ingenuity
The pairing of Next-Gen GPUs and DLSS 4 Are Redefining what we consider “realistic” in gaming.
It’s a symbiotic relationship where powerful hardware and advanced AI work together to unlock the 120 FPS, high-fidelity experience that players have long dreamed of.
This technology isn’t just about faster graphics; it’s about deeper immersion, better responsiveness, and a more cinematic experience that remains accessible.
Are we approaching the point where real-time game graphics are indistinguishable from reality, powered by this AI revolution? Share your thoughts on the future of photorealism in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a 120Hz monitor to benefit from 120 FPS?
Yes. To visually perceive the benefit of 120 FPS, your display must have a refresh rate of at least 120 Hertz (Hz). Otherwise, the monitor can only show 60 unique frames per second.
Is DLSS 4 available on all graphics cards?
No. DLSS 4, like previous iterations, requires the dedicated Tensor Cores found exclusively in the newest generation of NVIDIA’s architecture to run the complex AI algorithms necessary for upscaling and frame generation.
Does DLSS 4 add any input lag (latency)?
Frame Generation can introduce a small amount of latency because the frame is predicted, not natively rendered.
However, this is usually offset by companion technologies like NVIDIA Reflex, which actively reduces overall system latency to maintain responsiveness.
What is the difference between path tracing and ray tracing?
Path tracing is an advanced form of ray tracing. Ray tracing samples a limited number of light rays; path tracing samples a massive number of light paths, including complex light bounces, to create physically accurate, photo-realistic global illumination.
Will rival companies launch their own versions of DLSS 4?
Yes. AMD’s FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) and Intel’s XeSS are competitor technologies that achieve similar upscaling goals, often with wider hardware compatibility, though they typically use different methods than NVIDIA’s dedicated AI cores.
